|
映射用来定义文档及其字段如何被存储和索引,文档写入es时,es可根据写入内容的类型自动识别,这种机制就是动态映射(Dynamic field mapping),本文关注的是写入内容为字符串时,该内容被识别的字段类型;
环境信息
操作系统:Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS
elasticsearch:6.7.1
kibana:6.7.1
官网解释
来自官网的解释,如下图,地址是:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/dynamic-field-mapping.html
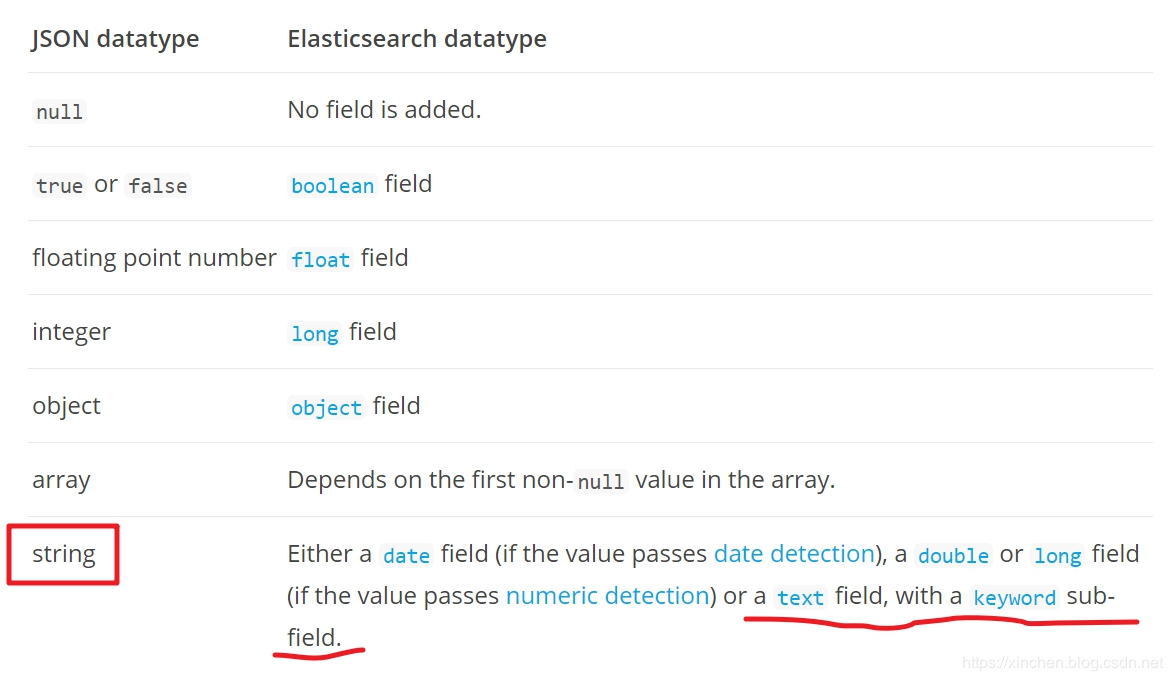
官网的解释为:
如果是日期类型,就映射为date;
如果是数字,就映射为double或者long;
否则就是text,并且还会带上keyword子类型;
映射为text好理解,但是带上keyword子类型怎么理解呢?应该是达到静态绑定的映射参数fields效果,让该字段有两种索引方式,这样可以用text类型做全文检索,再用keyword类型做聚合和排序;
接下来实战验证:
创建文档
在Kibana上执行以下命令,创建索引、类型、一个文档:
PUT book/es/101
{"title":"Elasticsearch IN ACTION","language":"java","author":"Radu Gheorghe","price":58.80,"publish_time":"2018-10-01","description":"本书主要展示如何使用Elasticsearch构建可扩展的搜索应用程序。"}
再创建一条:
PUT book/es/102
{"title":"ELK Stack权威指南 ","language":"java","author":"拉斐尔·酷奇","price":62.40,"publish_time":"2017-05-01","description":"本书涵盖了Elasticsearch的许多中高级功能。"}
检查动态映射结果
执行命令GET book/_mapping查看动态映射结果,字符串动态映射后,字段类型为text,但是都有了fields参数,里面是keyword的子类型:
{
"book" : {
"mappings" : {
"es" : {
"properties" : {
"author" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"description" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"language" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"price" : {
"type" : "float"
},
"publish_time" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
验证检索
执行以下检索命令验证检索:
GET book/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {"title":"Elasticsearch"}
}
}
第一条记录都可以搜索到,证明description字段已经被分词和索引了;
2. title字段还有一种索引方式keyword,也来试试,查keyword是要用完整内容做查询条件的,如下:
GET book/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {"title":"Elasticsearch IN ACTION"}
}
}
得到的结果如下,没有记录:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 0,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
这是怎么回事呢?对于这种sub-field的查询,不能直接使用title,而是要用title.keyword,改成如下请求:
GET book/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {"title.keyword":"Elasticsearch IN ACTION"}
}
}
这次顺利查到:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "es",
"_id" : "101",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Elasticsearch IN ACTION",
"language" : "java",
"author" : "Radu Gheorghe",
"price" : 58.8,
"publish_time" : "2018-10-01",
"description" : "本书主要展示如何使用Elasticsearch构建可扩展的搜索应用程序。"
}
}
]
}
}
验证聚合
执行以下命令,以language字段进行分组,统计每个分组的文档数:
GET book/_search
{
"aggs": {
"per_count": {
"terms":{
"field":"language.keyword"
}
}
}
}
得到结果如下,可以成功统计language字段为java的文档数量为2,可见动态映射给language设定的keyword类型能够直接用于聚合(text类型不能直接用于聚合,会返回status=400错误,修改参数后可以将text类用于聚合,但是会消耗更多内存资源):
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "es",
"_id" : "101",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Elasticsearch IN ACTION",
"language" : "java",
"author" : "Radu Gheorghe",
"price" : 58.8,
"publish_time" : "2018-10-01",
"description" : "本书主要展示如何使用Elasticsearch构建可扩展的搜索应用程序。"
}
},
{
"_index" : "book",
"_type" : "es",
"_id" : "102",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "ELK Stack权威指南 ",
"language" : "java",
"author" : "拉斐尔·酷奇",
"price" : 62.4,
"publish_time" : "2017-05-01",
"description" : "本书涵盖了Elasticsearch的许多中高级功能。"
}
}
]
},
"aggregations" : {
"per_count" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "java",
"doc_count" : 2
}
]
}
}
}
以上就是字符串在动态映射逻辑中的结果和验证,您使用动态映射的过程中,如果在词项查询和聚合等操作中遇到疑惑,希望本文能提供些参考;
(责任编辑:IT) |
