前言
Nginx是当前最流行的HTTP Server之一,根据W3Techs的统计,目前世界排名(根据Alexa)前100万的网站中,Nginx的占有率为6.8%。与Apache相比,Nginx在高并发情况下具有巨大的性能优势。
Nginx属于典型的微内核设计,其内核非常简洁和优雅,同时具有非常高的可扩展性。Nginx最初仅仅主要被用于做反向代理,后来随着HTTP核心的成熟和各种HTTP扩展模块的丰富,Nginx越来越多被用来取代Apache而单独承担HTTP Server的责任,例如目前淘宝内各个部门正越来越多使用Nginx取代Apache,据笔者了解,在腾讯和新浪等公司也存在类似情况。
同时,大量的第三方扩展模块也令Nginx越来越强大。例如,由淘宝的工程师清无(王晓哲)和春来(章亦春)所开发的nginx_lua_module可以将Lua语言嵌入到Nginx配置中,从而利用Lua极大增强了Nginx本身的编程能力,甚至可以不用配合其它脚本语言(如PHP或Python等),只靠Nginx本身就可以实现复杂业务的处理。而春来所开发的ngx_openresty更是通过集成LuaJIT等组件,将Nginx本身变成了一个完全的应用开发平台。目前淘宝数据平台与产品部量子统计的产品都是基于ngx_openresty所开发。对ngxin_lua_module或ngx_openresty感兴趣的朋友可以参考我在关键词上给出的链接,后续我也可能会写一些与其有关的文章。
本文将会重点关注Nginx模块开发入门及基础。目前Nginx的学习资料非常少,而扩展模块开发相关的资料几乎只有《Emiller's Guide To Nginx Module Development》一文,此文十分经典,但是由于Nginx版本的演进,其中少许内容可能有点过时。本文是笔者在研读这篇文章和Nginx源代码的基础上,对自己学习Nginx模块开发的一个总结。本文将通过一个完整的模块开发实例讲解Nginx模块开发的入门内容。
本文将基于Nginx最新的1.0.0版本,操作系统环境为Linux(Ubuntu10.10)。
前言
Nginx提要
Nginx在Linux下的安装与运行
Nginx配置文件基本结构
Nginx模块工作原理概述
Nginx模块开发实战
定义模块配置结构
定义指令
创建合并配置信息
编写Handler
组合Nginx Module
Nginx模块的安装
Nginx更深入的学习
Nginx参考文献
Nginx提要
开发Nginx扩展当然首要前提是对Nginx有一定的了解,然而本文并不打算详细阐述Nginx的方方面面,诸如Nginx的安装和各种详细配置等内容都可以在Nginx官网的Document中找到,本文在这里只会概括性描述一些后面可能会用到的原理和概念。
Nginx在Linux下的安装与运行
使用Nginx的第一步是下载Nginx源码包,例如1.0.0的下载地址为http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.0.0.tar.gz。下载完后用tar命令解压缩,进入目录后安装过程与Linux下通常步骤无异,例如我想讲Nginx安装到/usr/local/nginx下,则执行如下命令:
|
1
2
3
|
./configure --perfix=/usr/local/nginx
make
make install
|
安装完成后可以直接使用下面命令启动Nginx:
|
1
|
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
|
Nginx默认以Deamon进程启动,输入下列命令:
|
1
|
curl -i http://localhost/
|
就可以检测Nginx是否已经成功运行。或者也可以在浏览器中输入http://localhost/,应该可以看到Nginx的欢迎页面了。启动后如果想停止Nginx可以使用:
|
1
|
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
|
Nginx配置文件基本结构
配置文件可以看做是Nginx的灵魂,Nginx服务在启动时会读入配置文件,而后续几乎一切动作行为都是按照配置文件中的指令进行的,因此如果将Nginx本身看做一个计算机,那么Nginx的配置文件可以看成是全部的程序指令。
下面是一个Nginx配置文件的实例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
#user nobody;
worker_processes 8;
error_log logs/error.log;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /home/yefeng/www;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
|
Nginx配置文件是纯文本文件,你可以用任何文本编辑器如vim或emacs打开它,通常它会在nginx安装目录的conf下,如我的nginx安装在/usr/local/nginx,主配置文件默认放在/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。
其中“#”表示此行是注释,由于笔者为了学习扩展开发安装了一个纯净的Nginx,因此配置文件没有经过太多改动。
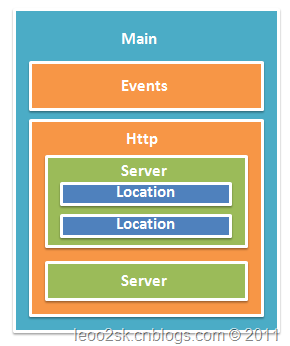
Nginx的配置文件是以block的形式组织的,一个block通常使用大括号“{}”表示。block分为几个层级,整个配置文件为main层级,这是最大的层级;在main层级下可以有event、http等层级,而http中又会有server block,server block中可以包含location block。
每个层级可以有自己的指令(Directive),例如worker_processes是一个main层级指令,它指定Nginx服务的Worker进程数量。有的指令只能在一个层级中配置,如worker_processes只能存在于main中,而有的指令可以存在于多个层级,在这种情况下,子block会继承父block的配置,同时如果子block配置了与父block不同的指令,则会覆盖掉父block的配置。指令的格式是“指令名 参数1 参数2 … 参数N;”,注意参数间可用任意数量空格分隔,最后要加分号。
在开发Nginx HTTP扩展模块过程中,需要特别注意的是main、server和location三个层级,因为扩展模块通常允许指定新的配置指令在这三个层级中。
最后要提到的是配置文件是可以包含的,如上面配置文件中“include mime.types”就包含了mine.types这个配置文件,此文件指定了各种HTTP Content-type。
一般来说,一个server block表示一个Host,而里面的一个location则代表一个路由映射规则,这两个block可以说是HTTP配置的核心。
下图是Nginx配置文件通常结构图示。
关于Nginx配置的更多内容请参看Nginx官方文档。
Nginx模块工作原理概述
(Nginx本身支持多种模块,如HTTP模块、EVENT模块和MAIL模块,本文只讨论HTTP模块)
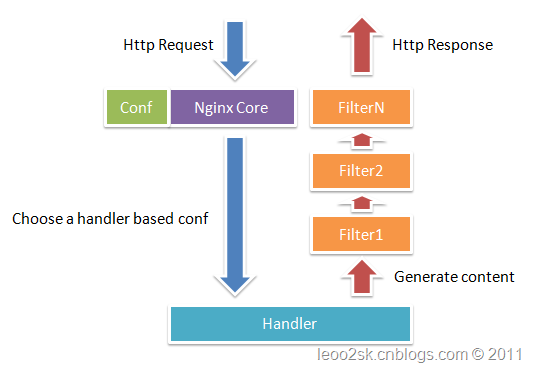
Nginx本身做的工作实际很少,当它接到一个HTTP请求时,它仅仅是通过查找配置文件将此次请求映射到一个location block,而此location中所配置的各个指令则会启动不同的模块去完成工作,因此模块可以看做Nginx真正的劳动工作者。通常一个location中的指令会涉及一个handler模块和多个filter模块(当然,多个location可以复用同一个模块)。handler模块负责处理请求,完成响应内容的生成,而filter模块对响应内容进行处理。因此Nginx模块开发分为handler开发和filter开发(本文不考虑load-balancer模块)。下图展示了一次常规请求和响应的过程。
Nginx模块开发实战
下面本文展示一个简单的Nginx模块开发全过程,我们开发一个叫echo的handler模块,这个模块功能非常简单,它接收“echo”指令,指令可指定一个字符串参数,模块会输出这个字符串作为HTTP响应。例如,做如下配置:
|
1
2
3
|
location /echo {
echo "hello nginx";
}
|
则访问http://hostname/echo时会输出hello nginx。
直观来看,要实现这个功能需要三步:1、读入配置文件中echo指令及其参数;2、进行HTTP包装(添加HTTP头等工作);3、将结果返回给客户端。下面本文将分部介绍整个模块的开发过程。
定义模块配置结构
首先我们需要一个结构用于存储从配置文件中读进来的相关指令参数,即模块配置信息结构。根据Nginx模块开发规则,这个结构的命名规则为ngx_http_[module-name]_[main|srv|loc]_conf_t。其中main、srv和loc分别用于表示同一模块在三层block中的配置信息。这里我们的echo模块只需要运行在loc层级下,需要存储一个字符串参数,因此我们可以定义如下的模块配置:
|
1
2
3
|
typedef struct {
ngx_str_t ed;
} ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t;
|
其中字段ed用于存储echo指令指定的需要输出的字符串。注意这里ed的类型,在Nginx模块开发中使用ngx_str_t类型表示字符串,这个类型定义在core/ngx_string中:
|
1
2
3
4
|
typedef struct {
size_t len;
u_char *data;
} ngx_str_t;
|
其中两个字段分别表示字符串的长度和数据起始地址。注意在Nginx源代码中对数据类型进行了别称定义,如ngx_int_t为intptr_t的别称,为了保持一致,在开发Nginx模块时也应该使用这些Nginx源码定义的类型而不要使用C原生类型。除了ngx_str_t外,其它三个常用的nginx type分别为:
|
1
2
3
|
typedef intptr_t ngx_int_t;
typedef uintptr_t ngx_uint_t;
typedef intptr_t ngx_flag_t;
|
具体定义请参看core/ngx_config.h。关于intptr_t和uintptr_t请参考C99中的stdint.h或http://linux.die.net/man/3/intptr_t。
定义指令
一个Nginx模块往往接收一至多个指令,echo模块接收一个指令“echo”。Nginx模块使用一个ngx_command_t数组表示模块所能接收的所有模块,其中每一个元素表示一个条指令。ngx_command_t是ngx_command_s的一个别称(Nginx习惯于使用“_s”后缀命名结构体,然后typedef一个同名“_t”后缀名称作为此结构体的类型名),ngx_command_s定义在core/ngx_config_file.h中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
struct ngx_command_s {
ngx_str_t name;
ngx_uint_t type;
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
ngx_uint_t conf;
ngx_uint_t offset;
void *post;
};
|
其中name是词条指令的名称,type使用掩码标志位方式配置指令参数,相关可用type定义在core/ngx_config_file.h中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#define NGX_CONF_NOARGS 0x00000001
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE1 0x00000002
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE2 0x00000004
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE3 0x00000008
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE4 0x00000010
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE5 0x00000020
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE6 0x00000040
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE7 0x00000080
#define NGX_CONF_MAX_ARGS 8
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE12 (NGX_CONF_TAKE1|NGX_CONF_TAKE2)
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE13 (NGX_CONF_TAKE1|NGX_CONF_TAKE3)
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE23 (NGX_CONF_TAKE2|NGX_CONF_TAKE3)
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE123 (NGX_CONF_TAKE1|NGX_CONF_TAKE2|NGX_CONF_TAKE3)
#define NGX_CONF_TAKE1234 (NGX_CONF_TAKE1|NGX_CONF_TAKE2|NGX_CONF_TAKE3 \
|NGX_CONF_TAKE4)
#define NGX_CONF_ARGS_NUMBER 0x000000ff
#define NGX_CONF_BLOCK 0x00000100
#define NGX_CONF_FLAG 0x00000200
#define NGX_CONF_ANY 0x00000400
#define NGX_CONF_1MORE 0x00000800
#define NGX_CONF_2MORE 0x00001000
#define NGX_CONF_MULTI 0x00002000
|
其中NGX_CONF_NOARGS表示此指令不接受参数,NGX_CON F_TAKE1-7表示精确接收1-7个,NGX_CONF_TAKE12表示接受1或2个参数,NGX_CONF_1MORE表示至少一个参数,NGX_CONF_FLAG表示接受“on|off”……
set是一个函数指针,用于指定一个参数转化函数,这个函数一般是将配置文件中相关指令的参数转化成需要的格式并存入配置结构体。Nginx预定义了一些转换函数,可以方便我们调用,这些函数定义在core/ngx_conf_file.h中,一般以“_slot”结尾,例如ngx_conf_set_flag_slot将“on或off”转换为“1或0”,再如ngx_conf_set_str_slot将裸字符串转化为ngx_str_t。
conf用于指定Nginx相应配置文件内存其实地址,一般可以通过内置常量指定,如NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,offset指定此条指令的参数的偏移量。
下面是echo模块的指令定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_echo_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("echo"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_http_echo,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t, ed),
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
|
指令数组的命名规则为ngx_http_[module-name]_commands,注意数组最后一个元素要是ngx_null_command结束。
参数转化函数的代码为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
static char *
ngx_http_echo(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_echo_handler;
ngx_conf_set_str_slot(cf,cmd,conf);
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
|
这个函数除了调用ngx_conf_set_str_slot转化echo指令的参数外,还将修改了核心模块配置(也就是这个location的配置),将其handler替换为我们编写的handler:ngx_http_echo_handler。这样就屏蔽了此location的默认handler,使用ngx_http_echo_handler产生HTTP响应。
创建合并配置信息
下一步是定义模块Context。
这里首先需要定义一个ngx_http_module_t类型的结构体变量,命名规则为ngx_http_[module-name]_module_ctx,这个结构主要用于定义各个Hook函数。下面是echo模块的context结构:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_echo_module_ctx = {
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
NULL, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
ngx_http_echo_create_loc_conf, /* create location configration */
ngx_http_echo_merge_loc_conf /* merge location configration */
};
|
可以看到一共有8个Hook注入点,分别会在不同时刻被Nginx调用,由于我们的模块仅仅用于location域,这里将不需要的注入点设为NULL即可。其中create_loc_conf用于初始化一个配置结构体,如为配置结构体分配内存等工作;merge_loc_conf用于将其父block的配置信息合并到此结构体中,也就是实现配置的继承。这两个函数会被Nginx自动调用。注意这里的命名规则:ngx_http_[module-name]_[create|merge]_[main|srv|loc]_conf。
下面是echo模块这个两个函数的代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
static void *
ngx_http_echo_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t));
if (conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
conf->ed.len = 0;
conf->ed.data = NULL;
return conf;
}
static char *
ngx_http_echo_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *prev = parent;
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *conf = child;
ngx_conf_merge_str_value(conf->ed, prev->ed, "");
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
|
其中ngx_pcalloc用于在Nginx内存池中分配一块空间,是pcalloc的一个包装。使用ngx_pcalloc分配的内存空间不必手工free,Nginx会自行管理,在适当是否释放。
create_loc_conf新建一个ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t,分配内存,并初始化其中的数据,然后返回这个结构的指针;merge_loc_conf将父block域的配置信息合并到create_loc_conf新建的配置结构体中。
其中ngx_conf_merge_str_value不是一个函数,而是一个宏,其定义在core/ngx_conf_file.h中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#define ngx_conf_merge_str_value(conf, prev, default) \
if (conf.data == NULL) { \
if (prev.data) { \
conf.len = prev.len; \
conf.data = prev.data; \
} else { \
conf.len = sizeof(default) - 1; \
conf.data = (u_char *) default; \
} \
}
|
同时可以看到,core/ngx_conf_file.h还定义了很多merge value的宏用于merge各种数据。它们的行为比较相似:使用prev填充conf,如果prev的数据为空则使用default填充。
编写Handler
下面的工作是编写handler。handler可以说是模块中真正干活的代码,它主要有以下四项职责:
读入模块配置。
处理功能业务。
产生HTTP header。
产生HTTP body。
下面先贴出echo模块的代码,然后通过分析代码的方式介绍如何实现这四步。这一块的代码比较复杂:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_echo_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_chain_t out;
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *elcf;
elcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_echo_module);
if(!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_HEAD|NGX_HTTP_GET|NGX_HTTP_POST)))
{
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/html") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *) "text/html";
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = elcf->ed.len;
if(r->method == NGX_HTTP_HEAD)
{
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if(rc != NGX_OK)
{
return rc;
}
}
b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
if(b == NULL)
{
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, r->connection->log, 0, "Failed to allocate response buffer.");
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
b->pos = elcf->ed.data;
b->last = elcf->ed.data + (elcf->ed.len);
b->memory = 1;
b->last_buf = 1;
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if(rc != NGX_OK)
{
return rc;
}
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
|
handler会接收一个ngx_http_request_t指针类型的参数,这个参数指向一个ngx_http_request_t结构体,此结构体存储了这次HTTP请求的一些信息,这个结构定义在http/ngx_http_request.h中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
struct ngx_http_request_s {
uint32_t signature; /* "HTTP" */
ngx_connection_t *connection;
void **ctx;
void **main_conf;
void **srv_conf;
void **loc_conf;
ngx_http_event_handler_pt read_event_handler;
ngx_http_event_handler_pt write_event_handler;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
ngx_http_cache_t *cache;
#endif
ngx_http_upstream_t *upstream;
ngx_array_t *upstream_states;
/* of ngx_http_upstream_state_t */
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_buf_t *header_in;
ngx_http_headers_in_t headers_in;
ngx_http_headers_out_t headers_out;
ngx_http_request_body_t *request_body;
time_t lingering_time;
time_t start_sec;
ngx_msec_t start_msec;
ngx_uint_t method;
ngx_uint_t http_version;
ngx_str_t request_line;
ngx_str_t uri;
ngx_str_t args;
ngx_str_t exten;
ngx_str_t unparsed_uri;
ngx_str_t method_name;
ngx_str_t http_protocol;
ngx_chain_t *out;
ngx_http_request_t *main;
ngx_http_request_t *parent;
ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed;
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest;
ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests;
ngx_http_virtual_names_t *virtual_names;
ngx_int_t phase_handler;
ngx_http_handler_pt content_handler;
ngx_uint_t access_code;
ngx_http_variable_value_t *variables;
/* ... */
}
|
由于ngx_http_request_s定义比较长,这里我只截取了一部分。可以看到里面有诸如uri,args和request_body等HTTP常用信息。这里需要特别注意的几个字段是headers_in、headers_out和chain,它们分别表示request header、response header和输出数据缓冲区链表(缓冲区链表是Nginx I/O中的重要内容,后面会单独介绍)。
第一步是获取模块配置信息,这一块只要简单使用ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf就可以了。
第二步是功能逻辑,因为echo模块非常简单,只是简单输出一个字符串,所以这里没有功能逻辑代码。
第三步是设置response header。Header内容可以通过填充headers_out实现,我们这里只设置了Content-type和Content-length等基本内容,ngx_http_headers_out_t定义了所有可以设置的HTTP Response Header信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
typedef struct {
ngx_list_t headers;
ngx_uint_t status;
ngx_str_t status_line;
ngx_table_elt_t *server;
ngx_table_elt_t *date;
ngx_table_elt_t *content_length;
ngx_table_elt_t *content_encoding;
ngx_table_elt_t *location;
ngx_table_elt_t *refresh;
ngx_table_elt_t *last_modified;
ngx_table_elt_t *content_range;
ngx_table_elt_t *accept_ranges;
ngx_table_elt_t *www_authenticate;
ngx_table_elt_t *expires;
ngx_table_elt_t *etag;
ngx_str_t *override_charset;
size_t content_type_len;
ngx_str_t content_type;
ngx_str_t charset;
u_char *content_type_lowcase;
ngx_uint_t content_type_hash;
ngx_array_t cache_control;
off_t content_length_n;
time_t date_time;
time_t last_modified_time;
} ngx_http_headers_out_t;
|
这里并不包含所有HTTP头信息,如果需要可以使用agentzh(春来)开发的Nginx模块HttpHeadersMore在指令中指定更多的Header头信息。
设置好头信息后使用ngx_http_send_header就可以将头信息输出,ngx_http_send_header接受一个ngx_http_request_t类型的参数。
第四步也是最重要的一步是输出Response body。这里首先要了解Nginx的I/O机制,Nginx允许handler一次产生一组输出,可以产生多次,Nginx将输出组织成一个单链表结构,链表中的每个节点是一个chain_t,定义在core/ngx_buf.h:
|
1
2
3
4
|
struct ngx_chain_s {
ngx_buf_t *buf;
ngx_chain_t *next;
};
|
其中ngx_chain_t是ngx_chain_s的别名,buf为某个数据缓冲区的指针,next指向下一个链表节点,可以看到这是一个非常简单的链表。ngx_buf_t的定义比较长而且很复杂,这里就不贴出来了,请自行参考core/ngx_buf.h。ngx_but_t中比较重要的是pos和last,分别表示要缓冲区数据在内存中的起始地址和结尾地址,这里我们将配置中字符串传进去,last_buf是一个位域,设为1表示此缓冲区是链表中最后一个元素,为0表示后面还有元素。因为我们只有一组数据,所以缓冲区链表中只有一个节点,如果需要输入多组数据可将各组数据放入不同缓冲区后插入到链表。下图展示了Nginx缓冲链表的结构:
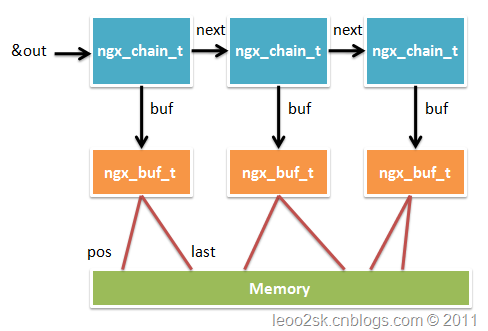
缓冲数据准备好后,用ngx_http_output_filter就可以输出了(会送到filter进行各种过滤处理)。ngx_http_output_filter的第一个参数为ngx_http_request_t结构,第二个为输出链表的起始地址&out。ngx_http_out_put_filter会遍历链表,输出所有数据。
以上就是handler的所有工作,请对照描述理解上面贴出的handler代码。
组合Nginx Module
上面完成了Nginx模块各种组件的开发下面就是将这些组合起来了。一个Nginx模块被定义为一个ngx_module_t结构,这个结构的字段很多,不过开头和结尾若干字段一般可以通过Nginx内置的宏去填充,下面是我们echo模块的模块主体定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
ngx_module_t ngx_http_echo_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_echo_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_echo_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
|
开头和结尾分别用NGX_MODULE_V1和NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING 填充了若干字段,就不去深究了。这里主要需要填入的信息从上到下以依次为context、指令数组、模块类型以及若干特定事件的回调处理函数(不需要可以置为NULL),其中内容还是比较好理解的,注意我们的echo是一个HTTP模块,所以这里类型是NGX_HTTP_MODULE,其它可用类型还有NGX_EVENT_MODULE(事件处理模块)和NGX_MAIL_MODULE(邮件模块)。
这样,整个echo模块就写好了,下面给出echo模块的完整代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
|
/*
* Copyright (C) Eric Zhang
*/
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_http.h>
/* Module config */
typedef struct {
ngx_str_t ed;
} ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t;
static char *ngx_http_echo(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
static void *ngx_http_echo_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static char *ngx_http_echo_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child);
/* Directives */
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_echo_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("echo"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_http_echo,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t, ed),
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
/* Http context of the module */
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_echo_module_ctx = {
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
NULL, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
ngx_http_echo_create_loc_conf, /* create location configration */
ngx_http_echo_merge_loc_conf /* merge location configration */
};
/* Module */
ngx_module_t ngx_http_echo_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_echo_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_echo_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
/* Handler function */
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_echo_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_chain_t out;
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *elcf;
elcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_echo_module);
if(!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_HEAD|NGX_HTTP_GET|NGX_HTTP_POST)))
{
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/html") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *) "text/html";
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = elcf->ed.len;
if(r->method == NGX_HTTP_HEAD)
{
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if(rc != NGX_OK)
{
return rc;
}
}
b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
if(b == NULL)
{
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, r->connection->log, 0, "Failed to allocate response buffer.");
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
b->pos = elcf->ed.data;
b->last = elcf->ed.data + (elcf->ed.len);
b->memory = 1;
b->last_buf = 1;
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if(rc != NGX_OK)
{
return rc;
}
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
static char *
ngx_http_echo(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_echo_handler;
ngx_conf_set_str_slot(cf,cmd,conf);
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
static void *
ngx_http_echo_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t));
if (conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
conf->ed.len = 0;
conf->ed.data = NULL;
return conf;
}
static char *
ngx_http_echo_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *prev = parent;
ngx_http_echo_loc_conf_t *conf = child;
ngx_conf_merge_str_value(conf->ed, prev->ed, "");
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
|
Nginx模块的安装
Nginx不支持动态链接模块,所以安装模块需要将模块代码与Nginx源代码进行重新编译。安装模块的步骤如下:
1、编写模块config文件,这个文件需要放在和模块源代码文件放在同一目录下。文件内容如下:
|
1
2
3
|
ngx_addon_name=模块完整名称
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES 模块完整名称"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/源代码文件名"
|
2、进入Nginx源代码,使用下面命令编译安装
|
1
2
3
|
./configure --prefix=安装目录 --add-module=模块源代码文件目录
make
make install
|
这样就完成安装了,例如,我的源代码文件放在/home/yefeng/ngxdev/ngx_http_echo下,我的config文件为:
|
1
2
3
|
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http_echo_module
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES ngx_http_echo_module"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http_echo_module.c"
|
编译安装命令为:
|
1
2
3
|
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --add-module=/home/yefeng/ngxdev/ngx_http_echo
make
sudo make install
|
这样echo模块就被安装在我的Nginx上了,下面测试一下,修改配置文件,增加以下一项配置:
|
1
2
3
|
location /echo {
echo "This is my first nginx module!!!";
}
|
然后用curl测试一下:
|
1
|
curl -i http://localhost/echo
|
结果如下:
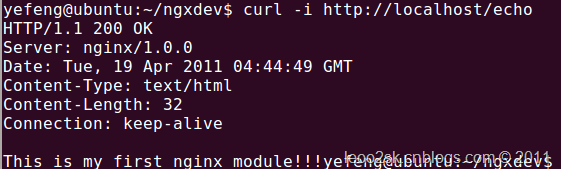
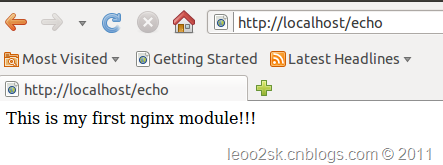
可以看到模块已经正常工作了,也可以在浏览器中打开网址,就可以看到结果:
更深入的学习
本文只是简要介绍了Nginx模块的开发过程,由于篇幅的原因,不能面面俱到。因为目前Nginx的学习资料很少,如果读者希望更深入学习Nginx的原理及模块开发,那么阅读源代码是最好的办法。在Nginx源代码的core/下放有Nginx的核心代码,对理解Nginx的内部工作机制非常有帮助,http/目录下有Nginx HTTP相关的实现,http/module下放有大量内置http模块,可供读者学习模块的开发,另外在http://wiki.nginx.org/3rdPartyModules上有大量优秀的第三方模块,也是非常好的学习资料。
如有意见建议或疑问欢迎发送邮件至ericzhang.buaa@gmail.com。希望本文对您有所帮助!!!
参考文献
[1] Evan Miller, Emiller's Guide To Nginx Module Development.http://www.evanmiller.org/nginx-modules-guide.html, 2009
[2] http://wiki.nginx.org/Configuration
[3] Clément Nedelcu, Nginx Http Server. Packt Publishing, 2010
(责任编辑:IT) |





