CentOS上使用MRTG监测网络设备流量情况
时间:2014-05-04 22:20 来源:linux.it.net.cn 作者:it
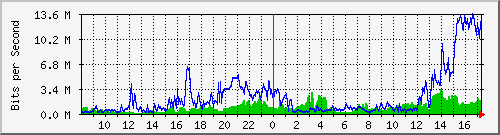
MRTG是一个开源的图形化的监控网络流量负载的工具(是德国OETIKER+PARTNER AG提供开源项目其中之一,http://oss.oetiker.ch/mrtg/ ),通过snmp协议得到设备的流量信息,并将流量负载以包含PNG格式的图形的HTML 文档以WEB方式显示给用户,以非常直观的形式显示流量负载(如下图)。
在X86架构的服务器上布置时,如果直接用系统里的YUM来安装是非常简单方便的一件事。而如果用SRC来完成,就得了解它所需要的支持如PERL、GD、LIBPNG、ZLIB了。
本文作者以自身实验来描述用YUM加载安装包完成的过程:
安装 MRTG
指令
yum -y install mrtg net-snmp*
由于我的网页发布是Apache的,所以如果没有该服务的需要加装它。
MRTG组件安装后会创建:
一个简单的配置文件( /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg )、
crontab档( /etc/cron.d/mrtg )、
及Apache配置文件( /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf )。
接下就是编辑 mrtg.cfg 文件。有两种方法:
一、只需删除注释,然后修改它们指向你要监视的设备。那需要你对MIB或OID信息有相当的了解,如果有可能以后补充。
二、也是我做的一种,相对简单。只需要使用cfgmaker,可以让 MRTG 自动创建一个mrtg.cfg(配置文件)。使用的方法如下:
使用cfgmaker
指令
cfgmaker public@192.168.0.1 > /etc/mrtg/mrtg.conf
public是IP为192.168.0.1这台设备SNMP的公共读出名;当然,你也可以将管道送往一个事先准备的其它文件,这样修改好后在CP过来。
自动生成的mrtg.conf文件中缺少Workpath,需要自己根据MRTG在APACHE的工作目录进行修改。
由于crontab档在安装时就已经是完整的,没有特殊要求就无需修改了。如果你和我一样着急看结果,就是本文最上面的那种流量监测图,可以在完成所有设置后进行一次
调试
指令
LANG=C LC_ALL=C /usr/bin/mrtg /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg --lock-file /var/lock/mrtg/mrtg_l --confcache-file /var/lib/mrtg/mrtg.ok
由于MRTG是通过APACHE发布的,之后需要根据实际情况修改APACHE用的配置文件( /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf )。而MRTG在Apache的设置里只缺省了localhost可以WEB方式查看URL。如果需要在另一台机器上访问(我这里是所有机器都可以访问)这个URL,需要修改MRTG的Apache配置文件并重新引导Apache。
修改MRTG的Apache设置
指令
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf
Alias /mrtg /var/www/mrtg
<Location /mrtg>
Order deny,allow
# Deny from all
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
Allow from all
# Allow from .example.com
</Location>
重新引导Apache服务
指令
service httpd restart
在APACHE的默认WEB页工作目录( /var/www )下会有一个mrtg目录,其中index.html文件并不存在。可以用MRTG组件中的 Indexmaker 来创建它(Indexmaker指令帮助见http://mrtg.cs.pu.edu.tw/doc/indexmaker.en.html)。你可以将以下指令加到crontab内,或者在每次修改mrtg.cfg后执行它。
创建索引页
指令
indexmaker --output=/var/www/mrtg/index.html /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg
现在一些都已完成,应该可以用浏览器打开 http://你的服务网址/mrtg 来查看图表。
需要注意的事:除MRTG外,OETIKER+PARTNER AG开源项目(Tobi Oetiker, 2011-09-13记录)还有RDtool、SmokePing、RemOcular、Extopus、SpreadButler、DbToRia、OP Tools和OP SEPP。
-
RDtool - The Round Robin Database Tool
 All you need for time series data storage and graphing. Write your own custom network or application monitoring script in minutes or use one of the many pre-made solutions based on RRDtool.
All you need for time series data storage and graphing. Write your own custom network or application monitoring script in minutes or use one of the many pre-made solutions based on RRDtool.
-
SmokePing - The Deluxe Latency Monitor
Probe for network and application latency. Identify hot spots, see trends developing, send alarms for critical conditions.
-
RemOcular - Your Eyes in the Cloud
remOcular provides a AJAX web interface to Unix command line tools like traceroute, top, mpstat, .
-
Extopus - The Monitoring Aggregator
Extopus is an aggregating frontend to monitoring systems. Its plug-in architecture provides an easy route to integrating output from a wide array of monitoring systems into a single instance of Extopus.
-
SpreadButler - The Spreadsheet Publisher
Spreadbutler is an Ajax-based system for live integration of spreadsheet data into webpages indepent of the technology used to create the webpages themselves.
-
DbToRia - Database to Rich Internet Application
DbToRia provides a generic web interface to your database application without further coding.
-
OP Tools - System Administration Tools
Tools we use to make or life as system administrators easier and our customers happier.
-
OP SEPP - Software Deployment System
System to manage and deploy software packages on Un*x platforms. SEPP is able to take advantages of (de)central package storages, NFS, and auto-mounting and allows concurrent software versions.
(责任编辑:IT)
| MRTG是一个开源的图形化的监控网络流量负载的工具(是德国OETIKER+PARTNER AG提供开源项目其中之一,http://oss.oetiker.ch/mrtg/ ),通过snmp协议得到设备的流量信息,并将流量负载以包含PNG格式的图形的HTML 文档以WEB方式显示给用户,以非常直观的形式显示流量负载(如下图)。
在X86架构的服务器上布置时,如果直接用系统里的YUM来安装是非常简单方便的一件事。而如果用SRC来完成,就得了解它所需要的支持如PERL、GD、LIBPNG、ZLIB了。
本文作者以自身实验来描述用YUM加载安装包完成的过程: 安装 MRTG
指令 yum -y install mrtg net-snmp*
由于我的网页发布是Apache的,所以如果没有该服务的需要加装它。
MRTG组件安装后会创建: 一个简单的配置文件( /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg )、 crontab档( /etc/cron.d/mrtg )、 及Apache配置文件( /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf )。
接下就是编辑 mrtg.cfg 文件。有两种方法: 一、只需删除注释,然后修改它们指向你要监视的设备。那需要你对MIB或OID信息有相当的了解,如果有可能以后补充。 二、也是我做的一种,相对简单。只需要使用cfgmaker,可以让 MRTG 自动创建一个mrtg.cfg(配置文件)。使用的方法如下: 使用cfgmaker
指令 cfgmaker public@192.168.0.1 > /etc/mrtg/mrtg.conf public是IP为192.168.0.1这台设备SNMP的公共读出名;当然,你也可以将管道送往一个事先准备的其它文件,这样修改好后在CP过来。
自动生成的mrtg.conf文件中缺少Workpath,需要自己根据MRTG在APACHE的工作目录进行修改。
由于crontab档在安装时就已经是完整的,没有特殊要求就无需修改了。如果你和我一样着急看结果,就是本文最上面的那种流量监测图,可以在完成所有设置后进行一次 调试
指令 LANG=C LC_ALL=C /usr/bin/mrtg /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg --lock-file /var/lock/mrtg/mrtg_l --confcache-file /var/lib/mrtg/mrtg.ok
由于MRTG是通过APACHE发布的,之后需要根据实际情况修改APACHE用的配置文件( /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf )。而MRTG在Apache的设置里只缺省了localhost可以WEB方式查看URL。如果需要在另一台机器上访问(我这里是所有机器都可以访问)这个URL,需要修改MRTG的Apache配置文件并重新引导Apache。 修改MRTG的Apache设置
指令 vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/mrtg.conf
Alias /mrtg /var/www/mrtg <Location /mrtg> Order deny,allow # Deny from all # Allow from 127.0.0.1 # Allow from ::1 Allow from all # Allow from .example.com </Location> 重新引导Apache服务
指令 service httpd restart
在APACHE的默认WEB页工作目录( /var/www )下会有一个mrtg目录,其中index.html文件并不存在。可以用MRTG组件中的 Indexmaker 来创建它(Indexmaker指令帮助见http://mrtg.cs.pu.edu.tw/doc/indexmaker.en.html)。你可以将以下指令加到crontab内,或者在每次修改mrtg.cfg后执行它。 创建索引页
指令 indexmaker --output=/var/www/mrtg/index.html /etc/mrtg/mrtg.cfg
现在一些都已完成,应该可以用浏览器打开 http://你的服务网址/mrtg 来查看图表。
需要注意的事:除MRTG外,OETIKER+PARTNER AG开源项目(Tobi Oetiker, 2011-09-13记录)还有RDtool、SmokePing、RemOcular、Extopus、SpreadButler、DbToRia、OP Tools和OP SEPP。
(责任编辑:IT) |