使用mysql的update语句更新数据
时间:2015-12-16 15:20 来源:linux.it.net.cn 作者:IT
Summary: updating data is one of the most important tasks when you work with databases. In this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in database tables.
Introduction to MySQL UPDATE statement
The UPDATE statement is used to update existing data in tables. It can be used to change column values of a single row, a group of rows or all rows in a table.
The following illustrates the MySQL UPDATE statement syntax:
UPDATE [LOW_ PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_name [, table_name...]
SET column_name1 = expr1
[, column_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE condition]
Let’s examine the UPDATE statement in greater detail:
-
Followed by the
UPDATE keyword is the name of the table that you want to update data. In MySQL, you can change the data of multiple tables using a single UPDATE statement. If the UPDATE statement violates any integrity constraint, MySQL does not perform the update and issues an error message.
-
The
SET clause determines the column names of the table and the new values. The new values could be literal values, result of expressions or subqueries.
-
The WHERE clause determines which rows will be updated. It is an optional element of the
UPDATE statement. If the WHEREclause is omitted, all rows in the table will be updated. The WHERE clause is so important that you should not forget. Sometimes, you may want to change just one row of the table; if you forget the WHERE clause, the UPDATE statement will update all the rows, which is not what you expected.
-
The
LOW_PRIORITY keyword is used to delay the execution until no other connections read data from the table. It is used for controlling the update process in MySQL database server.
-
The
IGNORE keyword is used to execute the update even there is an error occurred during the execution of the UPDATEstatement. The error in the update process could be duplicate value on a unique column, the new value does not match with the column’s data type, etc.
MySQL UPDATE examples
Let’s practice with a couple of examples in the MySQL sample database.
MySQL UPDATE a single column in a table
In this example, we are going to update the email of Mary Patterson to the new emailmary.patterso@classicmodelcars.com.
First, to make sure that we update the email successfully, we query Mary’s email using the SELECT statement as follows:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
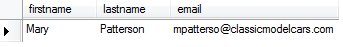
Second, we can update her current email to the new email mary.patterso@classicmodelcars.com using theUPDATE statement as the following query:
UPDATE employees
SET email = 'mary.patterso@classicmodelcars.com'
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
Because we just want to update Mary’s record so we use the WHERE clause to specify the Mary’s record ID 1056. The SET clause sets the email column value to the new email.
Third, we execute the SELECT statement again to verify the change.
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
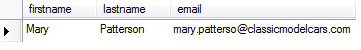
MySQL UPDATE multiple columns
To update multiple columns, you need to specify them in the SET clause. The following query updates both mary’s last name and email:
UPDATE employees
SET lastname = 'Hill',
email = 'mary.hill@classicmodelcars.com'
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056;
Le’ts check the changes:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056;
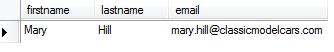
MySQL UPDATE from SELECT statement
You can provide the values for the SET clause from a SELECT statement that selects data from other tables. For example, first we check if is there any customer who does not have sales representative:
SELECT customername,
salesRepEmployeeNumber
FROM customers
WHERE salesRepEmployeeNumber IS NULL;
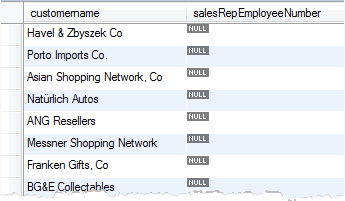
We can take any sale representative and update for those customers:
UPDATE customers
SET salesRepEmployeeNumber =
(
SELECT employeeNumber
FROM employees
WHERE jobtitle = 'Sales Rep'
LIMIT 1
)
WHERE salesRepEmployeeNumber IS NULL;
The SELECT statement returns an employee number of the employee whose job title is Sales Rep. The UPDATEstatement uses this employee number and update it for the customers whose sales representative is not available.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to use MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in database tables.
(责任编辑:IT)
Summary: updating data is one of the most important tasks when you work with databases. In this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in database tables. Introduction to MySQL UPDATE statement
The
The following illustrates the MySQL
UPDATE [LOW_ PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_name [, table_name...]
SET column_name1 = expr1
[, column_name2=expr2 ...]
[WHERE condition]
Let’s examine the
MySQL UPDATE examplesLet’s practice with a couple of examples in the MySQL sample database. MySQL UPDATE a single column in a table
In this example, we are going to update the email of First, to make sure that we update the email successfully, we query Mary’s email using the SELECT statement as follows:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
Second, we can update her current email to the new email
UPDATE employees
SET email = 'mary.patterso@classicmodelcars.com'
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
Because we just want to update Mary’s record so we use the
Third, we execute the
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056
MySQL UPDATE multiple columns
To update multiple columns, you need to specify them in the
UPDATE employees
SET lastname = 'Hill',
email = 'mary.hill@classicmodelcars.com'
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056;
Le’ts check the changes:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM employees
WHERE employeeNumber = 1056;
MySQL UPDATE from SELECT statement
You can provide the values for the
SELECT customername,
salesRepEmployeeNumber
FROM customers
WHERE salesRepEmployeeNumber IS NULL;
We can take any sale representative and update for those customers:
UPDATE customers
SET salesRepEmployeeNumber =
(
SELECT employeeNumber
FROM employees
WHERE jobtitle = 'Sales Rep'
LIMIT 1
)
WHERE salesRepEmployeeNumber IS NULL;
The In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to use MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in database tables. (责任编辑:IT) |