|
这篇文章主要介绍了Oracle中实现MySQL show index from table命令SQL脚本分享,本文只是模拟了Mysql中的show index from table命令 实验数据初始化:
create table t as select * from hr.employees; create index inx_t1 on t(employee_id,first_name desc,last_name); create index inx_t2 on t(job_id,hire_date);
显示该表所有索引的信息。 以dba登录
set linesize 300; set pagesize 100; col c1 format a20; col c2 format a20; col c3 format a20; col c4 format a20; col c5 format a20; col INDEX_NAME format a20; select INDEX_NAME, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,1,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c1, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,2,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c2, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,3,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c3, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,4,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c4, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,5,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c5 from ( select INDEX_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,COLUMN_LENGTH,COLUMN_POSITION,DESCEND from dba_ind_columns where table_owner='LIHUILIN' AND table_name='T' order by INDEX_NAME,column_position ) group by INDEX_NAME;
以普通用户登录
set linesize 300; set pagesize 100; col c1 format a20; col c2 format a20; col c3 format a20; col c4 format a20; col c5 format a20; col INDEX_NAME format a20; select INDEX_NAME, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,1,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c1, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,2,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c2, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,3,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c3, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,4,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c4, max(decode(COLUMN_POSITION,5,COLUMN_NAME||','||COLUMN_LENGTH||','||DESCEND,null)) c5 from ( select INDEX_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,COLUMN_LENGTH,COLUMN_POSITION,DESCEND from user_ind_columns where table_name='T' order by INDEX_NAME,column_position ) group by INDEX_NAME;
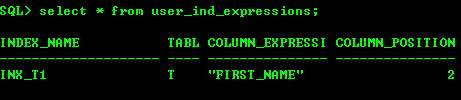
但是可以看到,以倒序创建的索引字段,都是以SYS等命名。 Oracle把这种倒序创建的索引字段看成函数索引。 它的信息保存在user_ind_expressions视图。
user_ind_expressions视图的COLUMN_EXPRESSION字段类型是long型。 王工的版本可以解决这个问题
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION long_2_varchar ( p_index_name IN user_ind_expressions.index_name%TYPE, p_table_name IN user_ind_expressions.table_name%TYPE, p_COLUMN_POSITION IN user_ind_expressions.table_name%TYPE) RETURN VARCHAR2 AS l_COLUMN_EXPRESSION LONG; BEGIN SELECT COLUMN_EXPRESSION INTO l_COLUMN_EXPRESSION FROM user_ind_expressions WHERE index_name = p_index_name AND table_name = p_table_name AND COLUMN_POSITION = p_COLUMN_POSITION;
RETURN SUBSTR (l_COLUMN_EXPRESSION, 1, 4000); set linesize 300; set pagesize 100; col c1 format a20; col c2 format a20; col c3 format a20; col c4 format a20; col c5 format a20; col INDEX_NAME format a20; SELECT INDEX_NAME, MAX (DECODE (COLUMN_POSITION, 1, COLUMN_NAME || ' ' || DESCEND, NULL)) c1, MAX (DECODE (COLUMN_POSITION, 2, COLUMN_NAME || ' ' || DESCEND, NULL)) c2, MAX (DECODE (COLUMN_POSITION, 3, COLUMN_NAME || ' ' || DESCEND, NULL)) c3, MAX (DECODE (COLUMN_POSITION, 4, COLUMN_NAME || ' ' || DESCEND, NULL)) c4, MAX (DECODE (COLUMN_POSITION, 5, COLUMN_NAME || ' ' || DESCEND, NULL)) c5 FROM ( SELECT a.INDEX_NAME, REPLACE ( DECODE ( descend, 'DESC', long_2_varchar (b.index_name, b.table_NAME, b.COLUMN_POSITION), a.column_name), '"', '') COLUMN_NAME, a.COLUMN_LENGTH, a.COLUMN_POSITION, DESCEND FROM user_ind_columns a LEFT JOIN user_ind_expressions b ON a.index_name = b.index_name AND a.table_name = b.table_name WHERE a.table_name = 'T' ORDER BY INDEX_NAME, column_position) GROUP BY INDEX_NAME;
(责任编辑:IT) |