|
循环控制之for循环
语法结构1
for Variable in List
do
commands
done
语法结构2
for Variable in List;do
commands
done
这个List可以为列表、变量、命令 等等
for循环 事先提供一个元素列表,而后,使用变量去遍历此元素列表,每访问一个元素,就执行一次循环体,直到元素访问完毕
1、for循环中的List为列表
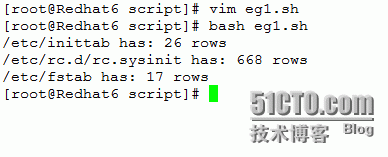
eg1: 显示/etc/inittab, /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit, /etc/fstab三个文件各有多少行;
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#!/bin/bash
forFile in/etc/inittab/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit /etc/fstab;do
Row=`wc-l $File | cut-d' '-f1`
echo"$File has: $Row rows"
done
|
运行结果
2、for循环中的List为变量
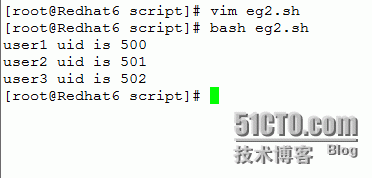
eg2:显示当前ID大于500的用户的用户名和id;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#!/bin/bash
useradduser1
useradduser2
useradduser3
Id=`cat/etc/passwd| awk-F: '{print $3}'`
forVar in$Id;do
if[ $Var -ge500 ];then
User=`grep"$Var\>"/etc/passwd| cut-d: -f1`
echo"$User uid is $Var"
fi
done
|
运行结果
3、for循环中的List为命令
eg3:显示当前shell为bash的用户的用户名和shell。
显示结果为 Bash user:root,/bin/bash
分析:先通过以bash结尾的shell来确定用户,然后把这些用户一个一个的输出
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#!/bin/bash
forVar in`grep"bash\>"/etc/passwd| cut-d: -f7`;do
User=`grep"$Var"/etc/passwd|cut-d: -f1`
done
Shell=`grep"bash\>"/etc/passwd|cut-d: -f7 |uniq`
forname in$User;do
echo"Bash user:$name,$Shell"
done
|
运行结果

4、for循环中的List为一连串的数字
eg4:分别计算1-100以内偶数(Even number)的和,奇数(Odd number)的和.
分析:当一个数与2取余用算时,为1则表示该数为奇数,反之为偶数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#!/bin/bash
EvenSum=0
OddSum=0
forI in`seq1 100`;do
if[ $[$I%2] -eq1 ]; then
OddSum=$[$OddSum+$I]
else
EvenSum=$[$EvenSum+$I]
fi
done
echo"EvenSum: $EvenSum."
echo"OddSUm: $OddSum."
|
运行结果

5、C语言格式的for循环
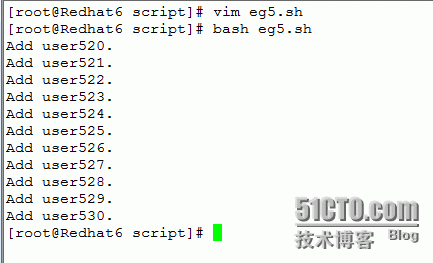
eg5:添加用户从user520添加到user530,且密码与用户名一样。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#!/bin/bash
for((i=520;i<=530;i++));do
useradduser$i
echo"Add user$i."
echouser$i | passwd-stdin user$i &>/dev/null
done
|
运行结果:(可以切换一个用户试试密码是否和用户名一样)
其他循环的格式如下,所有这些循环熟练掌握一种循环即可。
while循环命令的格式
while test command
do
other command
done
until循环的命令格式
until test command
do
other command
done
一个脚本的面试题 ,各位博友可以把您的答案回复在下面(大家一起交流)
通过传递一个参数,来显示当前系统上所有默认shell为bash的用户和默认shell为/sbin/nologin的用户,并统计各类shell下的用户总数。
运行如 bash eg.sh bash则显示结果如下
BASH,3users,they are:
root,redhat,gentoo,
运行如 bash eg.sh nologin则显示结果如下
NOLOGIN, 2users, they are:
bin,ftp,
(责任编辑:IT) |